The collateral costs of ransomware attacks commonly cost up to seven times more than the initial ransom payment, according to researchers at the security company Check Point.
The researchers, which analyzed data from several thousand cyberattacks, found that the cost of system restorations, monitoring efforts, and overall business disruption contributed to these total expenses.
The report also revealed that double extortion ransomware attacks are costing businesses more and more every year, suggesting that the need for effective cybersecurity tools has never been greater.
What Did The Ransomware Research Find?
Ransomware – a type of malware to denies users access to their data until they pay a ransom payment – is one of the fastest-growing cyber security threats facing businesses.
In the US, the average ransomware payment for victims totals more than $6 million, but according to new research from Check Point, this figure is only scraping the surface.
“Most other losses, including response and restoration costs, legal fees, monitoring costs, etc., are applied whether the extortion demand was paid or not. The year 2020 showed that the average total cost of a ransomware attack was more than seven times higher than the average ransom paid.” – Check Point
The IT security firm analyzed data from public sources and information obtained from the Kovrr database to identify the total cost of ransomware attacks. They found that the original ransom payment only costs businesses 15% of the total cost of attacks, with expenses like lost business opportunities, employee downtime, and legal costs making up the rest of the sum.
Check Point also found that threat actors appear to follow a specific pattern when determining how much to charge their victims. First, they assess the target’s financial records, and then they demand a fee that’s typically between 0.7% and 5% of their annual revenue.
Double Extortion Tactics Are Costing Businesses More
One reason why ransomware attacks are costing businesses more than ever is because of the growing use of double extortion tactics.
Double extortion, also referred to as ‘pay-now-or-get-breached’ is a strategy where criminals steal a victim’s data before encrypting their files. In doing so, malicious actors are able to threaten to leak or sell an individual or organization’s data if they refuse to pay the ransom.
This type of attack is bad news for any victim, but has a particularly grave impact on businesses. This is because organizations need to deal with the additional risk of lost customer data, and the massive implications this could have on consumer trust and brand reputation.
Unfortunately, due to the high cost of lost business, this means that companies struck with double extortion often will incur greater financial losses, even if they decide to pay the ransom in full.
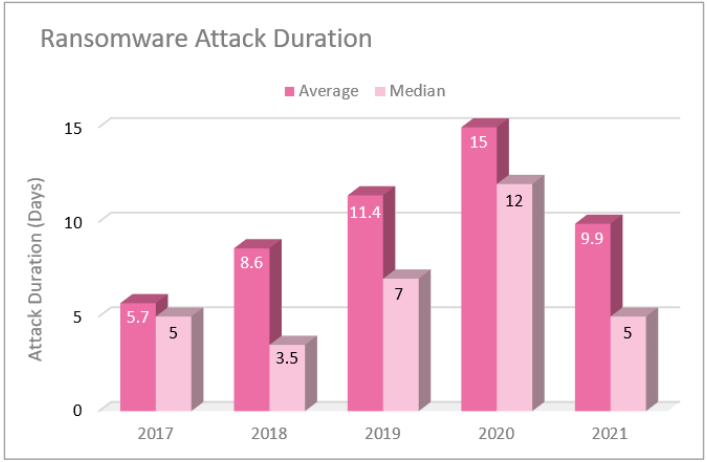
Despite the overall increase in double extortion attacks and ransomware payments, the research did appear to find a silver lining. In 2021, the duration of ransomware attacks appeared to significantly decrease. This suggests businesses are becoming better equipped at dealing with double-extortion ransomware.
But while minimizing the duration of these attacks is great, how can you avert them entirely?
Here’s How Your Business Can Prevent Ransomware Attacks
According to Check Point, preventing these incidents from happening in the first place is the best way to remain safe online. While you can’t stop yourself from being targeted, here’s how you can – of these ransomware attacks.
- Keep devices updated – It’s much easier for malicious actors to hack outdated systems. Stay one step ahead and regularly keep your software up to date.
- Invest in ransomware software – One of the simplest ways to evade online threats is to buy – and regularly update – antivirus software.
- Educate your workforce – Human error is a leading cause of security breaches. By educating your staff about the risks of ransomware, you can keep violations to a minimum.
- Use two-factor authentication – By protecting your data with more than a strong password, you can add an extra layer of mitigation between you and potential threats.




